放射線利用技術データベースのメインページへ
作成: 2002/01/08 水木 純一郎
データ番号 :040257
放射光X線を利用した電気化学における固液界面構造のその場観察
目的 :放射光X線を利用した電気化学における固液界面構造のその場観察
放射線の種別 :エックス線
放射線源 :電子シンクロトロン(8GeV, 100mA)
利用施設名 :SPring-8
概要 :
電気化学における反応のフロントである電極と電解液との界面構造を、放射光X線を利用して原子レベルで解析するものである。X線回折用の特別な電気化学セルを製作し、電極に電界を負荷することにより原子層制御された電極上への結晶成長を観察する。
詳細説明 :
放射光X線が利用できるようになって以来、急速に発展した研究分野に表面・界面構造が挙げられる。これは、X線強度が実験室系X線源に比べて数桁強いことが大きな理由である。特に固液界面構造解析は、表面構造研究に威力を発揮していたX線以外のほとんどのプローブは利用できず、放射光X線に期待するところが大きい。
電気化学における固体/液体界面は、電極と電解質との共存系であり、この界面をよぎって電位勾配の中での電子のやり取り、化学種の変化や移動、吸着、界面自体の化学変化が起こっている反応のフロントといえる。これらを理解、制御するためには、物理、化学、あるいは物理化学の領域を越えた他の領域の知識までも必要とし、境界領域の新しい学問分野と位置付けてもいいであろう。
具体的な対象としては、電解合成、燃料電池、電析、電解研磨、センサー、コロイド科学、腐食、防食など基礎的分野から応用分野までをカバーしている。これら電気化学分野を研究対象とする場合、実際に電位がかかり電流が流れている状態が生きた電極であり、電解質から引き上げた電極は死んだものであることを考えると、動作状態下であるin situでの観察が重要となる。すなわち、高強度の放射光X線が必要となる。
精密な表面・界面構造解析には電子線やX線による回折実験が必要である。この中でX線は、電子線のように超高真空環境を必要とせず、また透過性が高いため、詳細な液体/固体界面構造研究には唯一のプローブといっても過言ではない。そこで図1に示すようなX線回折用電気化学セルを準備することによって、電極に電圧を負荷させている状態下でのX線回折実験が可能となり固液界面構造を解析することができる。
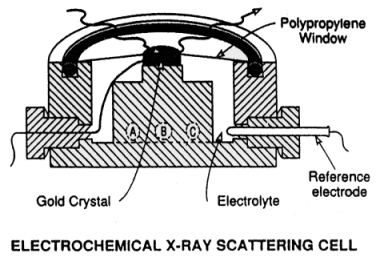
図1 X-ray scattering electrochemical cell. The Au(111) single crystal is held at the top center by a Kel-F clamp. The cell is sealed with a polypropylene window compressed against the Kel-F cell by an o-ring. (a) Electrolyte input; (b) counter electrode; (c) electrolyte output. An outer chamber (not shown) is filled with nitrogen gas to prevent diffusion of oxygen through the polypropylene window.(原論文1より引用)
例として1層のPd原子をAu(111)表面上に電析した場合の研究を示す。X線回折実験では、表面上の逆格子点から垂直方向に伸びる逆格子ロッド(L-方向)の回折X線強度を測定することにより、Au(111)面のAu層から垂直方向にどれだけ離れてPd原子層が電析し、さらに表面内Au原子位置に対してどのような位置(面内位置)にPdが成長するかを決定することができる。その様子を図2に示す。
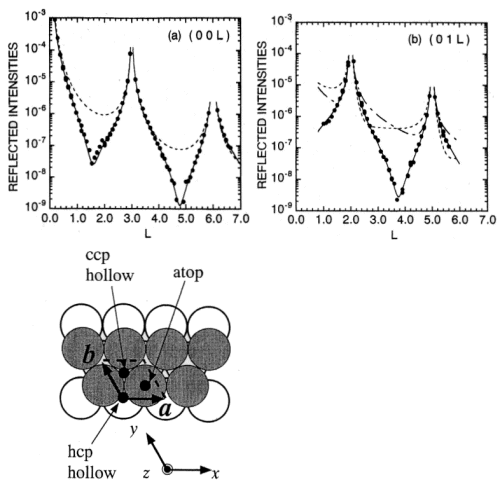
図2 The specular (a) and the non-specular (b) rod profiles for 1 ML Pd/Au(111). The solid lines are the best fit curves based on a pseudomorphic growth model. The dotted line in the specular rod profile represents the profile for the ideally terminated Au(111) surface. The dashed and dot-dashed lines in the non-specular rod profile were calculated for the Pd adsorption to the hcp threefold hollow site and the atop site, respectively, with the same surface normal structure as the best fit model. The bottom shows possible adsorption of Pd atoms on Au(111). Gray circle represent the Au atoms in the first layer and open circles represent the Au atoms in the second layer. The dashed parallelogram indicates the unit cell defined by the fundamental vectors a=a0(1/2, 0, 1/2)cubic, b=a0(-1/2, 1/2, 0)cubic and c=a0(1,1,1)cubic (a0=4.08 A). Note that the hexagonal coordinate system is employed. (原論文2より引用)
上の例では電極に負荷する電圧を制御することにより電析原子1層だけを電極上に成長させることができる、いわゆるUnder Potential Deposition (UPD)現象を利用した結晶成長である。このよく知られているUPD現象も電解液/電極界面構造をX線回折により詳細に解析することにより、実は理想的に界面が形成されているわけではなく、電析原子が基板中に拡散していることが明らかになってきている。図3にTe原子をAu(111)面上にUPD成長させた時のX線回折データを示す。Fittingから得られた結果は、最上表面原子層はTeが0.33原子層、Auが0.08原子層からできていることを示しており、原子拡散があることがわかる。
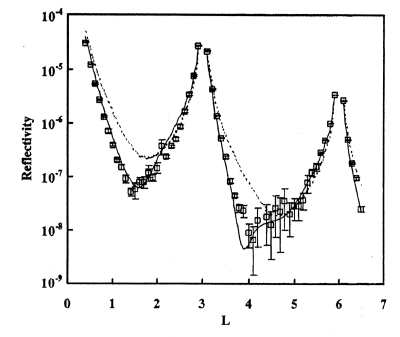
図3 Specular X-ray reflectivity from the Te UPD layer on the Au(111) substrate. The data collection was started 39 h after the UPD potential had been applied and lasted for 20 h in total. (square) Observed ddata. (---)The reflectivity expected for the top layer consisting of 0.33 ML Te and 0.02 ML Au. (-)The reflectivity expected for the top layer consisting of 0.33 ML Te and 0.08 ML Au. (原論文3より引用)
電気化学の分野では標準的な測定手法となっている電流-電圧特性(cycling voltammetry)からUPD成長と考えられている負荷電圧領域において、時間とともにTe原子が基板のAu中に僅かではあるが拡散していることがX線回折実験から解析された。このことは、たとえUPD条件下での電析であっても原子層レベルで平坦な界面が形成されていない場合があることを示唆しており、電気化学の基礎的分野だけでなく応用分野にまで重要な知見を与えた。
コメント :
電気化学における電解液/電極界面構造をX線回折により解析する場合、電極となる基板の表面状態が実験の成功のカギを握る。すなわち、できるだけ原子レベルで平坦な基板表面であることが重要である。実際の応用を考えるとそのような電極表面を使う場合はほとんど無く、電気化学における基礎研究という位置付けが正しい認識であろう。しかし、近年のナノに代表される電子デバイスに関係する機能性物質の作成に電気化学的手法が使われる可能性が大いにあり、その場合には実材料・デバイスを試料とした電気化学的手法によるin situ X線回折実験がデバイス開発に威力を発揮するであろう。
原論文1 Data source 1:
In situ x-ray-diffraction and -reflectivity studies of the Au(111)/electrolyte interface: Reconstruction and anion adsorption
Jia Wang, B. M. Ocko, Alison J. Davenport, Hugh S. Isaacs
Department of Physics, Brookhaven National Laboratory and Department of Applied Science, Brookhaven National Laboratory
Phys. Rev. 46 (No. 16), 10321-10338 (1992)
原論文2 Data source 2:
Pseudomorphic growth of Pd monolayer on Au(111) electrode surface
M. Takahasi, Y. Hayashi, J. Mizuki, K. Tamura, T. Kondo, H. Naohara, K. Uosaki
Department of Synchrotron Radiation Research, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and Division of Chemistry, Hokkaido University
Surface Science 461, 213-218 (2000)
原論文3 Data source 3:
Evidence for the diffusion of Au atoms into the Te UPD layer formed on a Au(111) substrate
H. Kawamura, M. Takahasi, N. Hojo, M. Miyake, K. Murase, K. Tamura, K. Uosaki, Y. Awakura, J. Mizuki, E. Matsubara
参考資料1 Reference 1:
The investigation of electrochemical systems with synchrotron radiation
Hans-Henning Srehblow ed.
Heinrich-Heine-Universitat
Synchrotron Radiation News 11 (No. 3) (1998)
キーワード:界面構造、X線回折、電気化学、その場観察、固液界面
interface structure, x-ray diffraction, electrochemistry,in-situ observation, solid/liquid interface
分類コード:040105, 040501, 040502
放射線利用技術データベースのメインページへ

