作成: 1998/08/30 栗原 正義
データ番号 :040144
2次イオン質量分析による深さプロフィールと高エネルギーイオンビーム分析との比較
目的 :2次イオン質量分析による深さプロフィールにおける各種の影響と精度改良について説明し、更に2次イオン質量分析と高エネルギーイオンビーム分析技術の関係に言及する。
放射線の種別 :軽イオン
放射線源 :CAMECA ims 4f SIMS、Cameca IMS-3F ion microscope、バンデグラーフ加速器、Quadrupole Perkin-Elmer PHI-6600 and Double Foucused Magnetic Sector VGIX70S
フルエンス(率):25 KeV 11B 2×1014 原子/cm2, 100 KeV 74Ge 2×1016 イオン/cm2
利用施設名 :フィリップス研究所(オランダ)、RCA研究所(米国)、西部オンタリオ大学(カナダ)、フロリダ大学(米国)
照射条件 :真空中
応用分野 :高エネルギーイオンビーム分析技術、深さ分析、表面トポグラフィー、多層金属酸化物膜分析、異種構造物質薄膜分析
概要 :
2次イオン質量分析(SIMS)による深さプロフィール分析における、1) 11Bを注入したSi(100)の表面トポグラフィーの影響、2)SiとAgを含む多層金属ー酸化物薄膜にXe 1次イオンによる精度改良、3)ZeSe、GaInP、SiGe/Feの様な異種構造薄膜の影響、等について取り上げる。
SIMSとラザフォード散乱分光(RBS)や核反応分析(NRA)のような高エネルギーイオンビーム分析技術の関係をレビューし、これらの分析技術が相互に補完し合い、分析結果に寄与すると指摘する。
詳細説明 :
2×1014原子/cm2フルエンス、25 KeV 11B を注入した10cm径のSi(100)ウエファを、サブミクロン以下の石版画に発生させた表面トポグラフィーでエッチングする。本試料について2次イオン質量分析(SIMS)で深さプロフィールを分析した。測定したボロン(B)濃度分布は標的の乱れていない平坦部の濃度分布と比べた。
図1は結果の1例であり、チャンネリング尾部を伴い殆どガウシアン分布に近く、深さ98nmの所に最大2×1019 11B/cm3の濃度分布を示す。更に、0.4%以下のB濃度が深さ350nm以上の所に分布する。図1には、 " flat " と名付けた未組織表面と0.7、0.5、0.3μm巾の溝をもつ3配列平行方向と垂直方向に対する11B濃度分布を示す。
要旨は次の通り。第1は、SIMSの深さプロフィイール解釈の多くは実際の濃度勾配が測定結果より急という考えによる。この絶対的仮定の妥当性の限界は調べる試料の局部的組織により定まる。第2は完成に近い集積回路の様なサブミクロンのチツプに対するSIMSの試みはその特有な表面構造のために難しい。
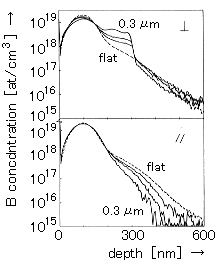
図1 Measured SIMS depth profiles of a 25 KeV 11B+ implantation in Si(100). The dashed curve, labeled "flat", is for an untextured surface. The other distributions were determined on a surface in which rectangular trenches had been etched after the implant. The trenches are separated from one another by approximately equally wide dykes. The results for three different widths, viz., 0.7 (-0.2) 0.3 μm, are displayed here. The larger deviations from the untextured profile occur for the smaller topography features. Two geometries are distinguished, with the 5.5 keV O2+ primary probe beam, impinging at nearly 45°on the surface, being aligned either parallel(‖)or perpendicular (⊥)to the trench direction. (原論文1より引用。 Reproduced from Appl. Phys. Lett., vol.57(22), 26 November (1990) p.2371-2373, A.J.Walker, M.T.Borchert, C.J.Vriezema, P.C.Zalm: Influence of surface topography on depth profiles obtained with secondary-ion mass spectrometry, Copyright (1990), with permission from American Institute of Physics and the authors.)
SIMS分析技術をラザフォード後方散乱(RBS)や核反応(NBS)の様な高エネルギー分析技術と比較した。表1はSIMS、RBS、NBAの各分析技術の長短所の定性的比較である。SIMSの長短所は補完関係を作りながらRBSやNBAの長短所と上手に緊密さを保つている。SIMSの長所は高感度、深さ分解能が良いこと、全元素検出能力、同位元素間を区別する能力、基本的特異性が良いことであり、短所は元素感度の変化、表面トポグラフィーの変形、イオン誘起原子混合効果等である。
研磨したTa基質上に陽極酸化的に成長させた0.32μm膜のTa2O5試料ではSIMSの深さ分解能について良い結果を示す。Ta金属に含む水素は多量で、酸化物の方に拡散する。SIMSの短所である元素の感度変化は標準試料との比較により解決される。
表1 Comparison of the strengths and weaknesses of secondary ion mass spectrometry, Rutherford backscattering spectrometry and nuclear reaction analysis.
(原論文2より引用。 Reproduced from Nucl. Instr. Meth. 191 (1981) 297-307, C.W.Magee: Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry and Iys Relation to High-Energy Ion Beam Analysis Techniques, Copyright (1981), with permission from Elsevier Science.)
-------------------------------------------------
Characteristics SIMS RBS NRA
-------------------------------------------------
Low Z sensitivity + - +
High Z sensitivity + + -
Depth resolution - surface + + +/-
Depth resolution - bulk + - -
Detection of all elements + - -
Elemental specificity + - +
Isotopic information + - +
Chemical information + - -
Multi-element analysis + + -
Quantitative with standards + + +
Quantitative without standards - + +
Depth scale with standards + + +
Depth scale without standards - + +
Matrix effects - + +
Simple spectra - + +
Lattice location information - + +
Matrix elemental analysis - + +
Trace elemental analysis + - -
Non-destructive - + +
Rapid + + -
Ion beam induced artifacts - + +
-------------------------------------------------
金属酸化物中にサンドイッチしたAgとCuを含む多層薄膜の深さプロフィールを種々の質量、エネルギーと化学反応度を用いSIMSにより調べ、RBSによる結果とも比較した。1次イオンとしてO2+又はO-を利用すると、ガラス界面上のZnO/Ag/ZnO薄膜のSIMSプロフィールでAgイオン強度分布に激しい歪みが見られた。3〜10KeVエネルギのO2+照射では、ガラス界面上でAgを検出、一方O-を利用するとRBSの結果の期待よりも外側表面で検出した。Ar+とXe+の1次ビームは、Zn/Ag/Zn分布に対して精確な深さプロフィールを与える。酸素を伴うTiO2/Cu/TiO2膜の深さプロフィールも又金属層に達した所で激しい歪みが生じ、これは6-9KeVエネルギーのXe+の1次イオンにより改良できた。酸素照射による歪み効果は電荷表面が引き起こす静電場における金属イオン移動により理解される。金属層のイオン化は酸素利用により促進され、希ガス利用は金属層からイオン生成を減らす。
異種構造をもつZnSe、GaInP、SiGe/Feについて磁気セクターと四重極型質量分析器をもつSIMSを用い深さプロフィールを調べた。ZnSe(2.67eV)の様に広いバンドギャツプをもつ半導体は青色光を発し、InGaP/CsAsはレーザーとして利用でき、高速Si1-xGexSi異種接合双極トランジスター(HBTs)は多方面に応用されている。半導体の薄膜析出パラメータと物理的・化学的性質の関係、特に薄膜異種構造の特性が不明確である。
図2は2×1016イオン/cm2、100KeVで74Geを注入し、1100℃で10秒焼鈍したSi試料のSIMS深さプロフィールを示す。表面近傍のSi分布はガウシアンであり、母地はGeで飽和していないことを示す。SiプロフィールはGeプロフィールの最大に対応する濃度尖端を示し、Geイオン注入によりSi1-xGex形成に関連する。
SIMSは半導体中の不純物とドーパント濃度の分析に強力な技術であり、薄膜異種構造に対しても優れた深さ分解能を示した。試料回転を伴う他のイオン源(O+,Ar+,Xe+及び液体Gaのようなもの)は破壊分析、工程制御、腐食等の様な研究にも柔軟な方法である。
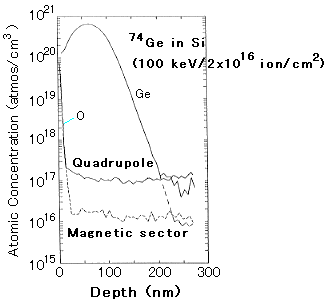
図2 SIMS the depth profiles of the Si sample implanted with 74Ge at 100keV with dose of 2×1016 ions/cm2 and with annealing at 1100℃ for 10 s with the quadruple(solid line) and the magnetic sector instruments(dotted line).
(原論文4より引用。 Reproduced from Vacuum, vol. 46, Nos.8-10, 1025-1029 (1995), E.O.Ristolainen, M.Puga-Lambers, B.Panthangay and P.H.Holloway: Depth profiling of thin film heterostructure materials by secondary ion mass spectrometry, Copyright (1995), with permission from Elsevier Science.)
コメント :
SIMSによる表面層の深さプロフィール分析3例を紹介し、併せてSIMSと類似分析法である、RBS, NBSとの関係を解説したレビューも取り上げた。レビューによれば、SIMSの長所はRBS、NBSの短所であり、逆にSIMSの短所はRBS、NBSの長所とされている。従って、これらの分析方法は相互補完によつて良い結果が得られるとしている。当分は相互補完による分析で進み、将来は各分析法の短所克服を期待したい。
原論文1 Data source 1:
Influence of surface topography on depth profiles obtained with secondary-ion mass spectrometry
A.J.Walker, M.T.Borchert, C.J.Vriezema and P.C.Zalm
Philips Research Laboratory, P.O. Box 80.000, 5600 JA Eindhoven, The Netherlands
Appl. Phys. Lett., vol.57(22), 26 November (1990) p.2371-2373
原論文2 Data source 2:
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry and Iys Relation to High-Energy Ion Beam Analysis Techniques
C.W.Magee
RCA Laboratories, Princeton, NJ 08450, USA
Nuclear Instruments and Methods, vol.191 (1981) 297-307
原論文3 Data source 3:
SIMS Depth Profiling of Multilayer Metal-Oxide Thin Films-Improved Accuracy Using a Xenon Primary Ion
N.S.McIntyre*), D.Johnston*), W.J.Chauvin*) and W.M.Lau*): K.Nietering2*) and D.Schuetzle2*); K.Shankar3*) and J.E.Macdonald3*)
*)Surface Science Western, University of Western Ontario, Natural Sciences Centre, London, Ontario, Canada N6A 5B7. 2*)Ford Motor Company, Dearborn, MI 48121, USA. 3*)Department of Physics, University of Guelph, Guelph, Ontario, Canada
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, B12 (1985) 389-395
原論文4 Data source 4:
Depth profiling of thin film heterostructure materials by secondary ion mass spectrometry
E.O.Ristolainen*) and M.Puga-Lambers2*), B.Panthangay2*) and P.H.Holloway2*)
*)Helsinki University of Technology, Center for Chemical Analysis, FIN-02150, Espoo, Finland. 2*)University of Florida, Depatment of Materials Science and Engineering, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA
Vacuum, vol.46, Nos.8-10, 1025-1029 (1995)
キーワード:2次イオン質量分析、深さプロフィール、表面トポグラフィー、多層金属酸化物薄膜、薄膜異種構造物質、高エネルギーイオンビーム分析技術
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry, DepthProfile, Surface Topography, Multilayer Metal-Oxide Thin Films, Thin Film Heterostructure Materials, High-Energy Ion Beam Analysis Techniques
分類コード:040101, 040405, 040501

